- Home
- Project Waste
- Statistics
- What's Wasted
- Why is it Wasted
- Material Lifecycle
- Recycling
- Landfill
- Smart Manufacture
- Design for Disassembly
- Simple Construction
- Avoiding Wasteful Techniques
- Legislation & Policy
- Case Studies
More intelligent ways of manufacturing and managing products must be implemented if waste is to ever truely be minimised and our resources sustained...
Overview
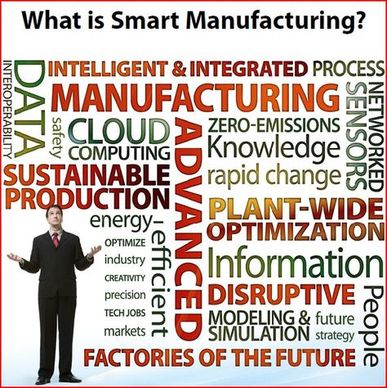
This page aims to educate on how techniques that can be easily integrated into any production line and investment in new product technologies later when required can reduce material wastage in any part of the process. This is known as Smart Manufacturing.
The use of this method can prevent material waste, human resource waste, energy waste and production expense. All which can be achieved by managing a production line optimally and investing in new technologies and materials.
Smart Manufacturing as a consequence is a method of preventing waste rather than that of using waste that has already been produced. Reduce as apposed to Recycling and Re-using.
The use of this method can prevent material waste, human resource waste, energy waste and production expense. All which can be achieved by managing a production line optimally and investing in new technologies and materials.
Smart Manufacturing as a consequence is a method of preventing waste rather than that of using waste that has already been produced. Reduce as apposed to Recycling and Re-using.
Smart Manufacturing
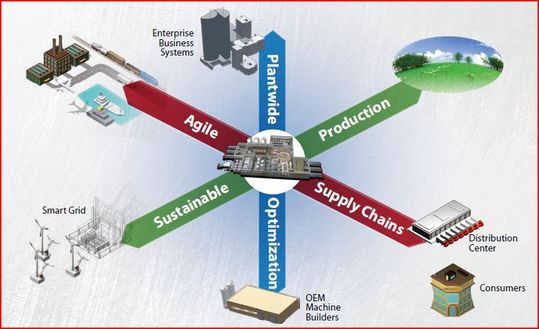
Phase 1 Factory-wide Data Integration

Smart manufacturing will interconnect and better manage all stages of a product process. This will advance plant-wide efficiency and optimize economic performance, worker safety and environmental sustainability.
Phase 2 Manufacturing Intelligence

The addition of high performance computing platforms (cloud computing) will enable factories to create optimum levels of manufacturing intelligence. Entire plants will run at variable speeds and productivity in order to conserve energy and increase outputs when required.
Phase 3 Product Innovation
As the factory intelligence grows and is coupled with advanced models of product processes, it can then be implemented in line with high-tech machinery such as Nanotechnology. This development then results in the aim of smart manufacturing, a disruption of the product market.
A more in depth piece published by
is available here
A method of Smart Manufacturing....... Lean Manufacturing
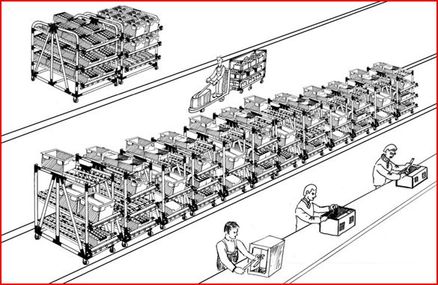
Current Manufacturing
Current manufacturing methods are traditionally coupled with problems of material wastage, unnecessary waiting, and excess inventory. All three of these forms of waste are usually products of the traditional “push” system. This is because “push” manufacturing keep producing and pushing the product on down the line no consideration is made as to whether there's demand or need for the product.
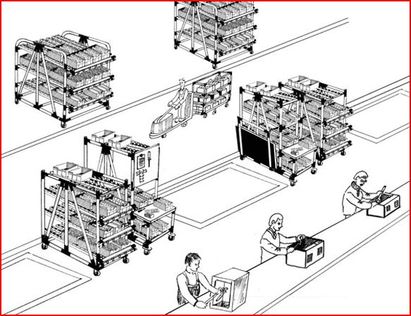
Lean Manufacturing (Basic Smart Manufacturing)
Lean manufacturing however utilizes a “pull” system where no more product is produced until the final step requires it, consequently the amount of product that is produced at each stage is dependent on demand at the next. In this way, consumer demand drives how much is essentially ‘pulled’ out of the factory, product to consumer. Lean manufacturing as a result also looks to reduce waste from production lines; identify, reduce, and then work toward eliminating waste.
Smart Manufacturing (Hi-Tech)
With the application of lean manufacturing to a production line, it is then possible as discussed at the top of the page to apply more advanced methodology to the plant. The integration of advanced machinery and computing can turn a factory line into a highly productive (when required) one. It can reduce packaging wastage as well as raw material wastage when creating the product, while mechanisation can provide a more fluent way of moving product down the line and creating quality items.
By Luke Matschke